Learning Activities for Instructional System Design - Part 1
These activities can easily be adapted to the classroom. Some activities, such as the one on Reflection, are best for individual performance, while others, such as the Presentation activity, would make a good small group activity. Also, at Ice Breakers, there is a ADDIE activity for introducing a class to each other.
Reflecting on the ISD Model
Listed below are five statements. Think about each statement carefully and then order each statement from 1 to 5, with 1 being what you enjoy doing the most, and 5 being what you enjoy doing the least. NOTE: You cannot use a number more than once
- __________ I enjoy investigative work, asking questions, studying and mapping processes, and documenting the correct steps for performing a task or process.
- __________ I enjoy planning and creating the blueprints or outlines for guiding a project.
- __________ Once the basic plans for a project have been created, I enjoy creating the necessary documents, procedures, etc. that form the project.
- __________ I enjoy coaching and helping others to excel at their jobs. You could say that I am a "people" person.
- __________ I enjoy researching a project to see that it is viable. I do not mind starting over when necessary.
Presenting the ISD Model
People learn in a number of different ways. For example, some people learn best by reading, while others like to see diagrams (pictures, models, etc.), and some even enjoy listening to others speak about the subject. Although we might learn best one way, seeing the same information in a variety of formats or mediums helps to reinforce the concepts. That is, we do not learn from just one media. As a trainer, you need to be able to present the same subject through several formats so everyone understands the concepts. See if you can express the ISD model in 2 or 3 different media. Spend about 30 to 45 minutes on this activity.
Using the Learning Domains with ISD
A committee of colleges studied learning and divided it into three major domains (categories):
- Cognitive - mental skills (Knowledge)
- Affective - growth in feelings or emotional areas (Attitude)
- Psychomotor - manual or physical skills (Skills)
These three domains are divided into other learning processes which will be discussed later. However, these three major domains are important to trainers as although a new behavior might be learned in a variety of methods, it can always be traced back to three major activities:
- Cognitive (Knowledge) - mental skills where the brain must be used to perform intellectual tasks.
- Affective (Attitude) - best described as "coming from the heart," - just because we know something, does not mean will act upon it.
- Psychomotor (Skills) - physical skills where the body must coordinate muscular activities (some are minor, such as turning a dial with your fingers).
By plotting the three learning domains in a matrix with the three main areas of HRD - training, development, and education, we can see what behaviors or goals will be produced. By using the chart below, answer the following questions:
- After training, you discover that your learners are not using their new skills on the job. You know they have the skills and abilities as you tested them. What learning domain should you concentrate your research efforts and what would you look for?
- Your manufacturing facility has a high turn-over rate. Your manager wants the training department to help improve the retention rate as it is getting harder and harder to hire new employees. One of the things your analysis has uncovered is that almost no ones is promoted from manufacturing into the other departments. What domains and HRD areas should you concentrate on and why?
- There seems to be very little teamwork in one of the departments within you organization. In fact, it is scorned by most of the other departments for having a very low productive rate. Its manager wants your training department to help pull the people together. During your analysis you discover that most of the sayings appear to be true. What area(s) should you concentrate on?
| Training | Education | Development | |
Skills (Psychomotor Domain) |
Perform tasks for present skill level Cross-training to meet organizational needs | Promotability - perform at higher skill levels Cross-training to meet personal needs (desire for growth) |
Personal tools such as teamwork and the ability to work with others (e.g. greet others in friendly manner, ask for help) |
|
Knowledge (Cognitive Domain) |
Perform tasks for present skill level Cross-training to meet organizational needs Increase problem solving ability |
Promotability - perform at higher cognitive levels Cross-training to meet personal needs (desire for growth) Process Improvement - Learn process modeling to improve and enrich present job |
Ability to adapt and work with others (e.g. read body language and tone of voice) Recognize and react to changes Leadership - Learn what makes a good leader (e.g. traits, tasks, principles) |
|
Attitude (Affective Domain) |
Motivation (perform tasks correctly after being trained) Practice good safety habits Belief in organization (e.g. good place to work, sense of belonging) |
Degree of personal desire to advance or contentment to stay at present job level Desire for process or task improvement (feels ownership) Willingness to accept change |
Diversity (e.g. acceptance of different cultures, religions, backgrounds) Be a champion of change (desire to be on the cutting edge of new technologies) Leadership - transfer leadership knowledge into actions that make others want to perform |
Study Questions
- How would you use ISD for generating long term strategy for meeting training needs?
- You want to implement an innovative training & development project that has not been done before. How can you use the ISD model to help you? How might it hinder you?
- How might a young start-up company's training needs differ from an established manufacturing firm?
- You manager wants you to "develop" a training program. Does this mean you should not do any analysis or design?
Answer Guide for Reflecting on the ISD Model
There in no right or wrong way to order the list. The list is in the same order as ADDIE (Analysis, Design, Development, Implement, Evaluate). This exercise is simply a method to help you to determine which steps of the ISD model you enjoy the most, and which steps you enjoy the least. The steps of the model that you number 4 and 5 should be the ones that you closely monitor when you do your first few ISD projects. The tasks that we enjoy doing the least are the tasks that often do not receive the full benefit of our attention.
Also, training developers must often work under time constraints, conflicting priorities, lack of resources, etc. Knowing your weak spots and the tasks that you do not enjoy as much will help you to focus on the priorities that must be accomplished, instead of what you like to perform.
Answer Guide for Presenting
There are a wide variety of ways to present the model. Listed below are three different methods.
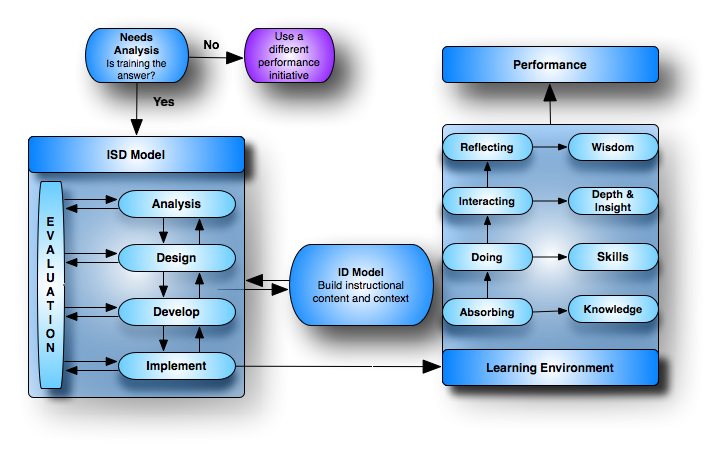
Mind mapThis image shows that the parts are all interrelated and that evaluation occurs throughout the entire implementation of the project. Also, if you can draw, then you might want to use pictures instead of words. For example, instead of using the word "Analysis," you might draw a microscope.
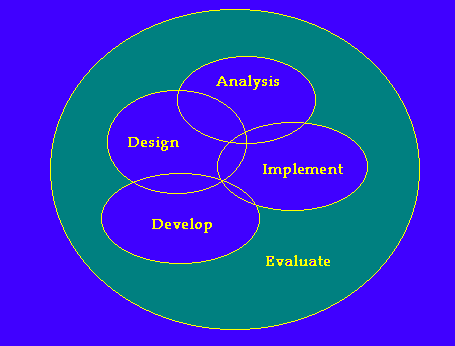
While this story compares ISD to building a house, similar stories can be built around other projects, hobbies, vacations, etc.
Several years back we built our first home. The first thing we had to do was to decide on a location, how to finance it, and what type of house to build (Analysis). Next we had to have an architecture firm design the blueprints for the builders to follow (Design). Once we had all the planning in place, the contractors started on the construction of our new home (Development). After it was completed we were finally able to move in (Implement). Throughout the whole process we evaluated the separate steps. For example, we did not just look at one bank for the financing, but at several so that we could find the best rate and people we trusted. We ensured the architectures incorporated what we wanted into the blueprints. When the builders started the construction, we and other inspectors ensured they followed established practices. Even today we inspect and repair our home to keep it in tip top shape.
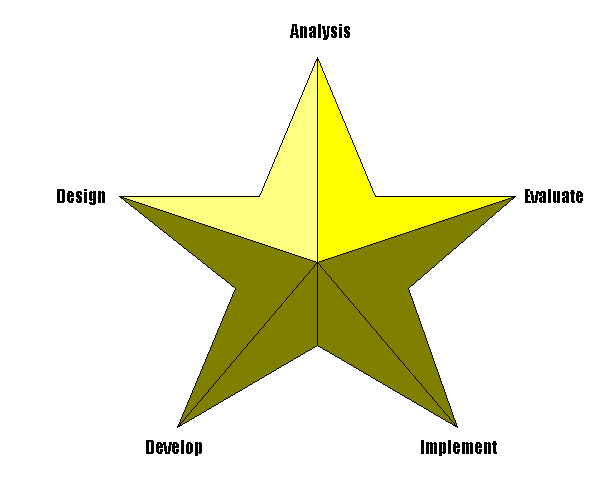
Model with a StoryFor centuries, sailors, shepherds, and other outdoor persons have relied upon the North Star to navigate their way through the seas and wilderness. By using the five pointed ADDIE Star, trainers can discover the most effective and efficient route for a learner to master a task:
Answer Guide for Learning Domains
- You should concentrate on the Affective Domain. Some of the things to look for are: A) Do they have the resources, such as time or the tools to perform the skill B) Is the new behavior being supported by their supervisor and coworkers C) Does the process support the new skill?
- You should work on all three of the domains under Education by helping the employees to: A) Learn new skills using the Psychomotor Domain B) Learn new problem solving skills under the Cognitive domain C) Show the employees that it will pay-off in learning something besides what they presently use on the job (affective).
- Your first area would be the Psychomotor domain under Development. The employees need to learn to work with others by using personal tools such as cooperation and esprit.
For more information on this topic, see: Blooms' Learning Domains
Answer Guide for Study Questions
Open questions such as these can be answered in a number of ways. Listed below are some of the more common type answers.
- How would you use ISD for generating long term strategy for meeting training needs? - Short term needs are basically met with training employees to perform in the present, while long term needs are met with aggressive development and education programs that will meet the organization's future needs.
- You want to implement an innovative training & development project that has not been done before. How can you use the ISD model to help you? - By showing in your analysis how it will benefit the organization and then using its design and development strengths to carry the project out on time and within budget. How might it hinder you? - By sticking too closely with the steps and not allowing the project to develop its own characteristics.
- How might a young start-up company's training needs differ from an established manufacturing firm? - Due to their rapid growth, young start-ups often need more of a Rapid Prototyping Design (RPD) development program, while established firms have a better picture of what they need in the future. But both of these methods can have their disadvantages; young firms need some of the stability of ISD for planning for the future, while older firms can become bogged down in traditional methods if they become afraid to use different development models.
- You manager wants you to "develop" a training program. Does this mean you should not do any analysis or design? - People often use the words "develop" or "design" or "implement" when what they really mean is that they want you to use the necessary means to create a viable training program. We often use one of these words to describe a project that we are working on. If you are not sure, then ask.
Next Steps
Go to the next chapter: Analysis
Return to the Table of Contents